February 11, 2025
February 11, 2025
Medical Waste Disposal: Best Practices for Healthcare Facilities
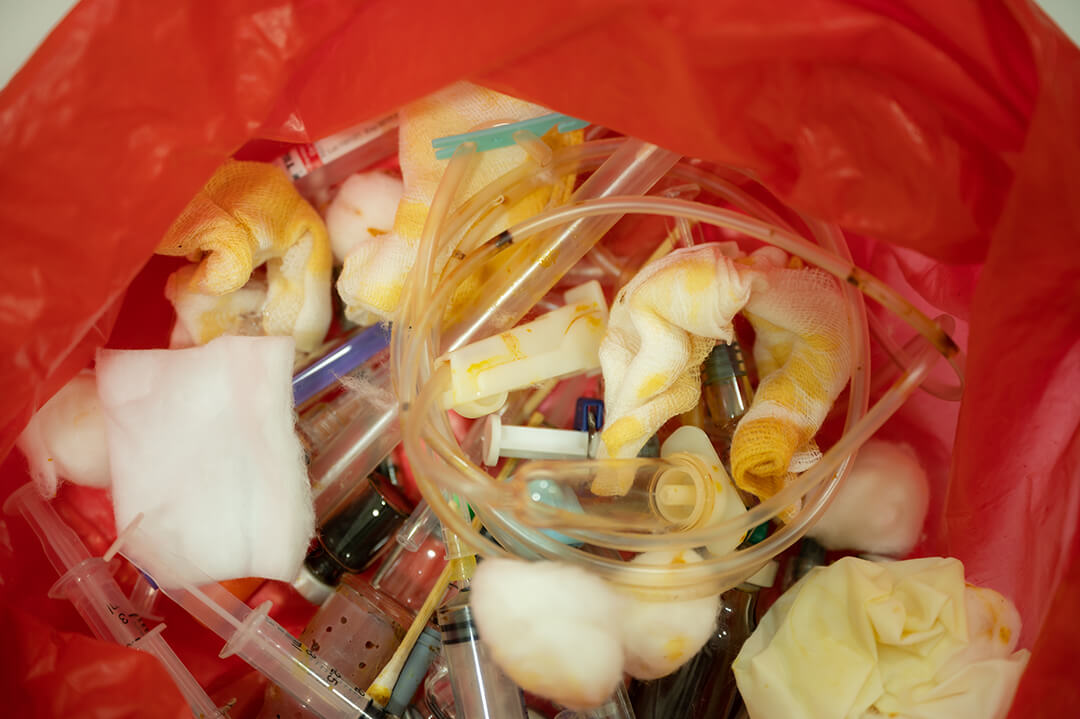
Medical waste poses unique challenges due to its potential for harboring infectious diseases. Improper disposal can have severe consequences for public health, the environment, and healthcare workers. Adhering to best practices in medical waste disposal is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance.
1. Waste Segregation:
- Categorization: Meticulous segregation of waste streams is paramount. Common categories include:
- Infectious waste: Contaminated with blood, body fluids, or pathogens (e.g., dressings, bandages, cultures).
- Pathological waste: Human or animal tissues, organs, and body parts.
- Sharps waste: Needles, syringes, scalpels, and other sharp objects.
- Pharmaceutical waste: Expired, unused, or contaminated medications.
- Chemical waste: Disinfectants, solvents, and other chemicals used in healthcare settings.
- Color-coding: Utilize color-coded bags or containers for easy identification and proper disposal.
2. On-site Storage:
- Secure Storage Areas: Designate secure, well-ventilated storage areas for medical waste, away from public access.
- Proper Containers: Use leak-proof, puncture-resistant containers for all waste types. Sharps containers must be specifically designed for sharps disposal.
- Labeling: Clearly label all containers with the type of waste, date, and originating department.
- Temperature Control: Store temperature-sensitive waste (e.g., pharmaceuticals) according to manufacturer guidelines.
3. Handling and Transportation:
- Employee Training: Ensure all staff receive comprehensive training on proper handling, storage, and transportation of medical waste.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide and enforce the use of appropriate PPE, such as gloves, gowns, and eye protection, when handling medical waste.
- Safe Transportation: Utilize dedicated vehicles for transporting medical waste, equipped with leak-proof containers and appropriate safety features.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to all applicable local, state, and federal regulations regarding medical waste transportation.
4. Treatment and Disposal:
- Treatment Methods: Select appropriate treatment methods based on the type of waste and regulatory requirements. Common methods include:
- Incineration: High-temperature incineration destroys most pathogens.
- Autoclaving: Steam sterilization effectively inactivates microorganisms.
- Chemical disinfection: Using chemicals to kill pathogens.
- Microwave disinfection: Utilizing microwave energy to heat and inactivate pathogens.
- Licensed Disposal: Engage with licensed and reputable medical waste disposal companies that adhere to all environmental regulations.
5. Record Keeping:
- Maintain Detailed Records: Maintain accurate records of all medical waste generated, stored, transported, and disposed of.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and best practices.
6. Waste Minimization:
- Source Reduction: Implement strategies to reduce the amount of medical waste generated, such as:
- Using reusable medical equipment whenever possible.
- Minimizing the use of single-use items.
- Implementing drug diversion programs to prevent medication waste.
- Recycling: Explore opportunities for recycling materials such as paper, plastics, and metals.
7. Emergency Preparedness:
- Develop a Spill Response Plan: Have a well-defined plan in place to address potential spills or accidents involving medical waste.
- Emergency Equipment: Ensure easy access to emergency equipment such as spill kits, absorbent materials, and protective gear.
8. Continuous Improvement:
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of waste management practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Staff Training: Provide ongoing training to staff on the latest best practices and any changes in regulations.
- Technology Integration: Explore the use of technology, such as electronic waste tracking systems, to improve efficiency and compliance.
By adhering to these best practices, healthcare facilities can ensure the safe and responsible management of medical waste, protecting public health, the environment, and their own staff.